Types of Dermal Filler Ingredients
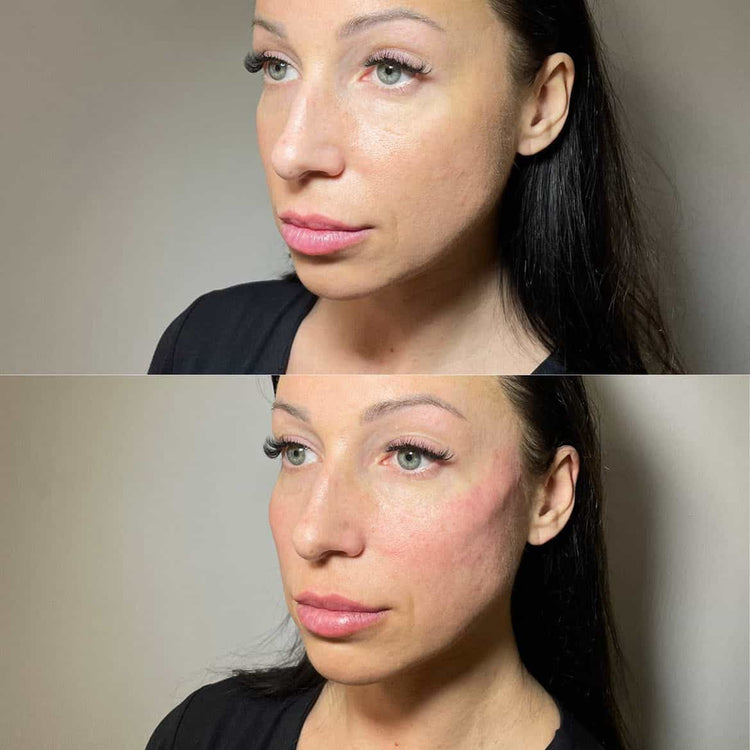
Dermal fillers are injectable substances used to enhance facial contours, reduce wrinkles, and restore volume. Their popularity stems from their ability to provide noticeable results with minimal downtime. But what exactly goes into these transformative injections?
Hyaluronic Acid
One of the most common dermal filler ingredients is hyaluronic acid (HA). HA is a naturally occurring substance found in the body’s skin, cartilage, and connective tissues. It acts like a sponge, attracting and holding water, which gives the skin its plumpness and elasticity.
Dermal fillers containing HA work by injecting this gel-like substance into the targeted areas, effectively adding volume and smoothing out wrinkles and fine lines.
Because HA is naturally found in the body, it’s generally well-tolerated and has a low risk of allergic reactions. It also degrades naturally over time, typically lasting anywhere from 6 to 18 months, depending on the product and individual factors.
Poly-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA)
Besides hyaluronic acid, another type of dermal filler ingredient is poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA).
- PLLA is a biodegradable synthetic polymer that stimulates collagen production.
- When injected, PLLA triggers the body’s natural healing response, leading to the gradual formation of new collagen fibers.
- This process gradually plumps up the skin, reducing the appearance of wrinkles and restoring volume.
PLLA fillers typically last longer than HA fillers, with results often lasting for 12 to 24 months or more.
Calcium Hydroxylapatite (CaHA)
Calcium Hydroxylapatite (CaHA) is a biocompatible material derived from calcium phosphate, found naturally in bone and teeth. In dermal filler form, it’s composed of microspheres suspended in a gel.
When injected, CaHA stimulates the body’s own collagen production.
This leads to gradual volume restoration, smoothing wrinkles and enhancing facial contours.
CaHA fillers are known for their long-lasting results, often persisting for 18 months or more.
Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) is another type of dermal filler ingredient. Unlike HA, PLLA, and CaHA, PMMA is a permanent filler.
It’s made up of tiny plastic beads suspended in a gel. When injected, these beads act as scaffolding, providing immediate volume and lifting.
Because it’s not biodegradable, PMMA fillers are designed to last indefinitely. However, this permanence comes with some risks.
PMMA fillers can have a higher risk of complications compared to other types of dermal fillers. These can include granulomas (lumps under the skin), infection, and migration of the beads, which may require surgical removal.
Safety Considerations
Dermal fillers offer a popular solution for enhancing facial appearance, but understanding their composition is crucial for making informed decisions about treatment.
Allergic Reactions
Safety considerations are paramount when using dermal fillers. It’s essential to consult a qualified and experienced healthcare professional who can assess your suitability for treatment and advise on the most appropriate type of filler for your needs.
Allergic reactions, though generally uncommon with hyaluronic acid-based fillers, can occur. It’s crucial to disclose any known allergies or sensitivities to your provider beforehand.
For individuals with a history of severe allergic reactions or autoimmune disorders, dermal filler treatments may pose a higher risk.
Infection Risk
Infection is a potential risk associated with any invasive procedure, including dermal filler injections. Proper sterilization techniques and asepsis during the procedure are crucial to minimize this risk.
Patients should also be instructed on proper aftercare practices to reduce the risk of infection, such as keeping the injection sites clean and avoiding touching or rubbing them.
Signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, pain, warmth, or drainage, should be reported to a healthcare professional immediately.
Side Effects and Complications
Dermal fillers can cause temporary side effects like bruising, swelling, redness, tenderness, and itching at the injection site. These usually subside within a few days to a week.
More serious complications, though rare, can occur. These include allergic reactions, infection, vascular occlusion (blockage of blood vessels), and granulomas (lumpy skin growths). It’s essential to choose a qualified and experienced injector who follows strict safety protocols to minimize these risks.
Long-term effects are generally not expected with hyaluronic acid fillers as they are naturally broken down by the body. However, with permanent fillers like PMMA, there is a risk of long-term complications such as migration or extrusion of the filler material, requiring further procedures for removal.
FDA Approval and Regulation
The FDA regulates dermal fillers through strict approval processes. Before a dermal filler can be marketed in the United States, manufacturers must submit comprehensive data demonstrating its safety and effectiveness.
The FDA evaluates this data through rigorous scientific review, including clinical trials involving human subjects. If the FDA determines that a dermal filler meets safety and efficacy standards, it grants approval for marketing.
Approved dermal fillers carry specific labeling instructions outlining indications, contraindications (conditions that preclude use), potential side effects, and recommended dosage. Healthcare professionals must adhere to these guidelines when administering dermal fillers.
The FDA also monitors the safety of approved dermal fillers after they are on the market through post-marketing surveillance programs. These programs collect reports of adverse events from healthcare providers and patients, allowing the FDA to identify any potential safety issues and take appropriate action if necessary.
Choosing a Reputable Practitioner
Choosing a reputable practitioner is paramount when considering dermal filler treatment. Look for a board-certified dermatologist, plastic surgeon, or licensed medical professional with extensive experience in administering dermal fillers.
Inquire about their training, certifications, and the number of procedures they have performed.
Review before and after photos of previous patients to assess their aesthetic style and your comfort level.
Don’t hesitate to ask questions about their safety protocols, sterilization practices, and the specific type of fillers they use.
A reputable practitioner will prioritize patient safety, thoroughly evaluate your medical history, discuss potential risks and benefits, and create a customized treatment plan tailored to your individual needs and goals.
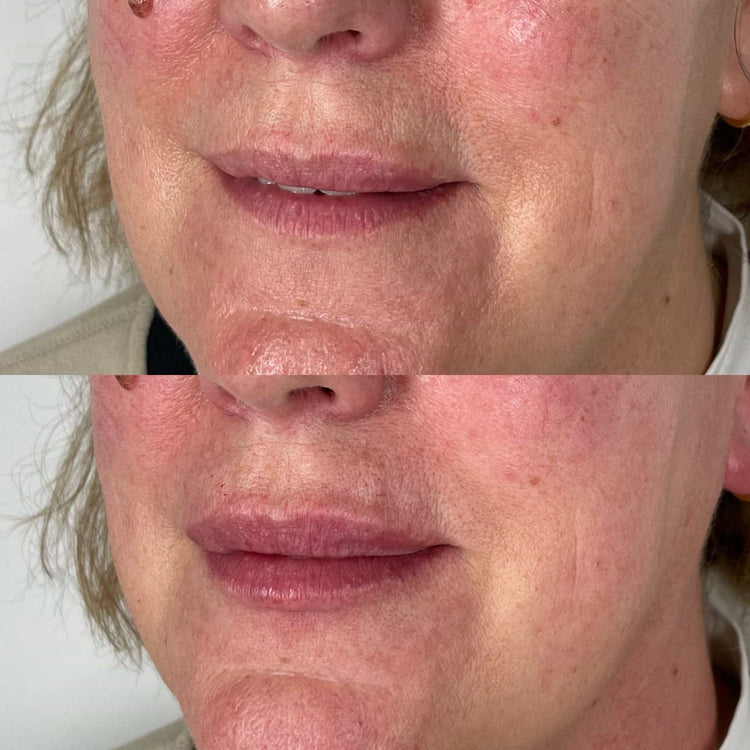
Long-Term Effects and Maintenance
Long-term effects of dermal fillers vary depending on the type of filler used. Hyaluronic acid fillers are temporary, typically lasting 6 to 18 months, as they are naturally broken down by the body. Poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) and calcium hydroxylapatite (CaHA), on the other hand, stimulate collagen production, leading to longer-lasting results that can persist for 12 to 24 months or more.
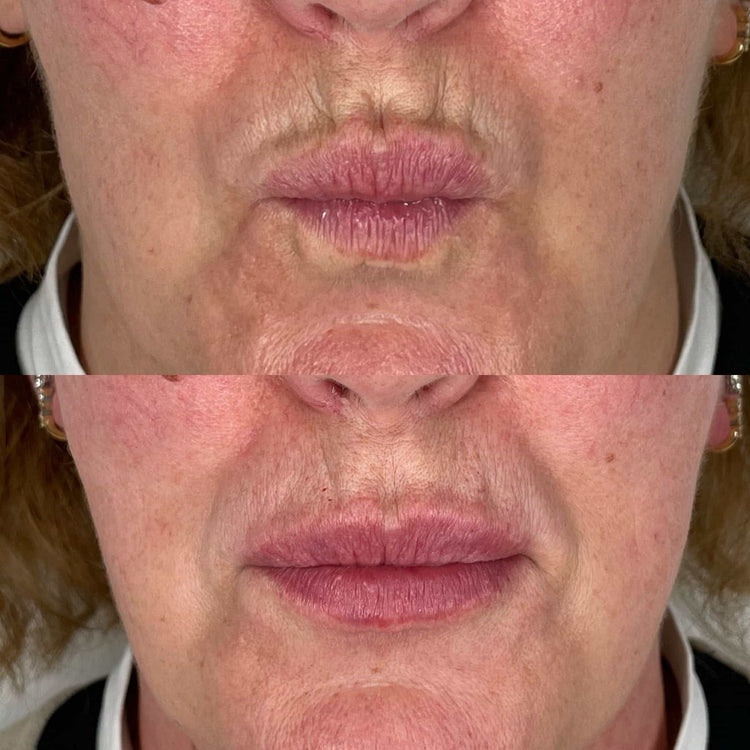
Permanent fillers, such as polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), are designed to last indefinitely. However, their permanence carries a higher risk of long-term complications like migration or extrusion of the filler material.
Maintenance of dermal filler results involves repeat treatments to replenish volume and address any fading or changes in appearance over time. The frequency of touch-up appointments depends on the type of filler used and individual factors such as skin elasticity and lifestyle.
Book your wrinkle-smoothing treatment with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me & You Clinic
- Why Are Kratom Gummies So Popular In Wellness Circles? - November 5, 2025
- What Is Tear Trough Filler Good For - November 4, 2025
- Weed Infused Juices For The Win - November 1, 2025
