Reserve a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Now
The Labiomental Groove: Understanding its Significance
Definition and Location
Schedule a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige
The Labiomental Groove, also known as the chin dimple, is a small depression found at the bottom of the lower lip, just above the mouth’s corner.
- It is a normal anatomical feature that can be present in people of all ages and ethnicities
- The Labiomental Groove is not unique to any particular gender or population group, although it may be more noticeable in some individuals due to facial structure or lip shape
Despite its normalcy, the Labiomental Groove can sometimes be a source of concern for those who experience psychological distress related to their appearance.
A definition of the Labiomental Groove is not necessarily straightforward, as it can manifest differently in various people. However, a common description is that it is a small indentation or crevice at the lower lip’s edge, typically around 1-2 centimeters deep and 0.5-1 centimeter wide.
When located centrally, the Labiomental Groove may appear as a slight hollow below the chin’s middle point, whereas when situated more laterally (toward the sides), it might be less noticeable or even absent altogether.
Interestingly, research has shown that the perception of the Labiomental Groove can vary depending on individual facial features and overall facial aesthetics. In some cases, people may be more aware of their Labiomental Groove due to personal preferences for facial symmetry or other aesthetic considerations.
Some argue that the Labiomental Groove is a small yet significant detail in the anatomy of the face, providing additional definition to the lower lip and chin area. Others view it as an imperfection that may need to be addressed through cosmetic procedures or surgical intervention.
From an evolutionary perspective, some researchers propose that the Labiomental Groove might serve as a subtle indicator of genetic variation among humans, although further study is needed to confirm this theory.
Aesthetically speaking, the Labiomental Groove can add character to a person’s face by creating visual interest at the lower lip region. However, when considered an imperfection or ‘blemish,’ it may also be perceived as a flaw that requires correction through various means such as fillers, surgery, or other cosmetic interventions.
Ultimately, whether or not one views the Labiomental Groove as significant depends on individual perspectives and standards of beauty. While some see it as an interesting anatomical feature worthy of recognition, others may view it as a minor imperfection that requires correction.
Anatomical Description
The Labiomental groove, also known as the chin dimple or mental fold, is a small depression located on the chin.
It is a unique anatomical feature that can be found in approximately 20-30% of the adult human population.
This groove is formed by the labium inferius muscle, which is one of the muscles of facial expression.
The Labiomental groove is not a true depression, but rather an indentation or a slight curvature of the chin’s skin and underlying bone.
Secure Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige
It is typically found on the lower part of the chin, near the mental protuberance (the bony prominence in front of the angle of the mandible).
The Labiomental groove can vary greatly in size, shape, and depth from one individual to another.
In some cases, it may be barely noticeable, while in others it can be quite deep.
Research has shown that the presence or absence of a Labiomental groove can have no significant effect on facial aesthetics or overall appearance.
However, its presence or absence can sometimes indicate genetic tendencies towards other facial features or characteristics.
The Labiomental groove is also sometimes associated with conditions such as hemifacial hypoplasia (a rare congenital disorder affecting the development of one side of the face).
In some cases, individuals with this condition may exhibit additional facial abnormalities.
From an anatomical perspective, the Labiomental groove is thought to be a vestigial remnant of the embryonic facial musculature.
This means that during fetal development, the muscles that would eventually form the Labiomental groove were present but later atrophied as they did not undergo significant growth or remodeling.
As a result, these remnants can remain visible on the chin after birth as small depressions or indentations.
Despite its relatively minor impact on facial aesthetics, the Labiomental groove has garnered attention in the field of craniofacial embryology and development.
Its unique characteristics make it an interesting subject for study and a useful indicator of genetic influences on facial morphology.
The labiomental groove is a small, Ushaped depression located in the lower lip, between the cupid’s bow (the curve of the upper lip) and the philtrum (the groove that runs from the nose to the mouth).
The Labiomental Groove is a small, U-shaped depression located in the lower lip, between the Cupid’s Bow (the curve of the upper lip) and the philtrum (the groove that runs from the nose to the mouth).
This anatomical feature is a significant aspect of facial morphology and plays a crucial role in various aspects of human communication, expression, and even behavior.
The Labiomental Groove is formed by the meeting point of the upper lip’s margin (the edge of the Cupid’s Bow) and the lower lip’s surface. This groove can be found in approximately 75-85% of the human population, with variations in size, shape, and depth depending on individual facial proportions.
From a functional perspective, the Labiomental Groove serves as an attachment point for various muscles responsible for lip movement and expression. The orbicularis oris muscle, which surrounds the mouth, attaches to the inner rim of the groove, enabling precise control over lip movements.
The significance of the Labiomental Groove extends beyond its functional role in facial expressions. Research suggests that this anatomical feature may be linked to various aspects of social behavior and emotional processing. For instance, studies have shown that individuals with more pronounced labiomental grooves tend to exhibit more exaggerated smiles and lip movements during social interactions.
From a psychological perspective, the Labiomental Groove has been associated with various personality traits and emotional states. Some researchers propose that a deeper or more pronounced groove may indicate increased emotional reactivity, while others suggest that a shallower groove may be linked to greater social anxiety.
Furthermore, the Labiomental Groove has been explored in various fields of study, including psychology, sociology, and anthropology. Researchers have used this feature as an indicator of genetic predispositions, cultural influences, and individual differences in facial expression patterns.
In conclusion, the Labiomental Groove is a fascinating anatomical feature that warrants further exploration and research. Its significance extends beyond its functional role in lip movement and expression, revealing insights into human communication, social behavior, emotional processing, and even psychological traits.
Embryological Development
The labiomental groove, also known as the marionette line, is a shallow furrow or depression found on the chin and lower lip region. It is a significant landmark in anatomy, particularly during facial development and embryology.
- The labiomental groove forms due to the fusion of the mandibular arches during fetal development. The first arch gives rise to the jaw, while the second arch contributes to the formation of the hyoid bone and muscles involved in swallowing.
During embryological development, the facial mesenchyme undergoes a series of complex transformations to give rise to the adult face. The labiomental groove is one of the key structures that emerge from this process.
- The groove is thought to be influenced by the interactions between the first and second pharyngeal arches, as well as the underlying facial muscles.
From a clinical perspective, the labiomental groove can provide valuable information about an individual’s facial development and growth. For example:
- A deep or well-defined groove may indicate a higher degree of fetal development, which could be beneficial for future dental or orthodontic treatment.
On the other hand, a shallow or poorly defined groove may suggest some level of developmental delay or irregularity.
- Additionally, the labiomental groove can also serve as an important landmark in surgical procedures involving the chin and lower lip region.
From a functional perspective, the labiomental groove plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity of the face. It helps to:
- Guide the movement of the lower lip during speech and eating.
This complex structure is also significant for dentists and orthodontists who study facial development and growth patterns. By examining the labiomental groove, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into an individual’s unique characteristics and develop more effective treatment plans.
The labiomental groove forms during embryonic development, around 68 weeks into gestation. It is a normal variation in human anatomy and serves as a landmark for various facial expressions.
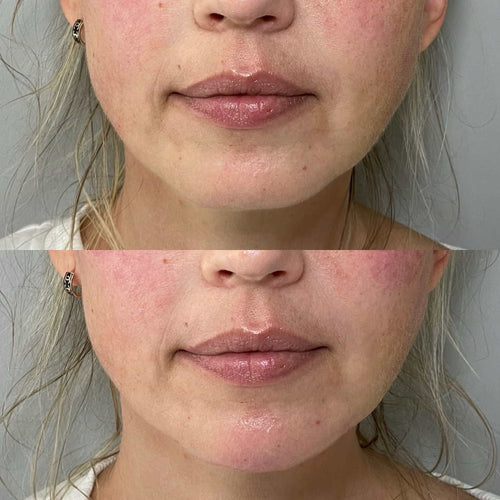
The labiomental groove, also known as the chin dimple or mental protuberance, is a shallow depression found in the lower lip region. It forms during embryonic development, typically around 68 weeks into gestation.
This anatomical variation occurs due to the way the tissues of the face develop and differentiate during fetal growth. The labiomental groove is characterized by a slight indentation or dimple on either side of the chin, just above the mental protuberance (the prominent bone at the chin).
Despite its name, the labiomental groove does not necessarily form into a distinct depression until after birth. Instead, it often remains as a subtle impression on the skin that can be more pronounced in some individuals than others.
Interestingly, the presence and depth of the labiomental groove do not typically affect facial function or aesthetics. It is considered a normal anatomical variation and is often seen in people of various ethnic backgrounds.
However, the labiomental groove can play a significant role in certain medical and dental procedures. For example, it can serve as an important landmark for surgeons during facial rejuvenation surgeries or for orthodontists when placing braces or other appliances on teeth.
In addition, the labiomental groove is sometimes used to assess facial symmetry and aesthetics in individuals undergoing cosmetic procedures. A well-defined labiomental groove can be a sign of good facial balance and proportions.
From a developmental perspective, the formation of the labiomental groove is thought to be related to the way the skin and underlying tissues of the face develop during embryonic growth. The groove itself may reflect the patterns of muscle attachment and movement in this region.
Researchers have also explored the potential connections between the labiomental groove and other facial features, such as the nasolabial fold (a deep crease that runs from the nose to the mouth) or the shape of the chin.
Further studies are needed to fully understand the significance of the labiomental groove in human anatomy and its relationship to various medical and dental conditions. However, for now, it remains a fascinating example of how subtle variations in facial anatomy can influence our appearance and function.
Functions and Importance
The Labiomental Groove is a unique anatomical feature of the human face that plays a significant role in articulation, expression, and aesthetics. Located on the lower lip, just below the mouth corner, this groove serves as a critical interface between the skin and underlying soft tissues.
Functions of the Labiomental Groove:
- The Labiomental Groove acts as a pathway for muscle fibers to connect with the chin and lower lip muscles, facilitating precise articulation of words and sounds. This groove helps to amplify and modify the acoustic output of speech, thereby enhancing intelligibility.
- During expression, the Labiomental Groove becomes more pronounced, creating an indentation in the skin that can convey emotions and attitudes through subtle variations in depth and shape.
- The groove also plays a role in the formation of words, particularly those involving the “l” and “r” sounds. The way the lip and chin interact within this groove influences the pronunciation of these sounds, with slight changes in the groove’s shape affecting the sound’s articulation.
Significance in Language English:
- The Labiomental Groove is essential for speech production, particularly for words with “l” and “r” sounds. Its unique shape and function allow for precise articulation of these sounds, which are critical components of the English language.
- A well-defined groove enables more accurate pronunciation of words, reducing the likelihood of mispronunciation or confusion between similar-sounding words.
- The Labiomental Groove also influences the intelligibility of speech in various contexts, such as in noisy environments or when speaking to individuals with hearing impairments.
Importance in Aesthetics and Expression:
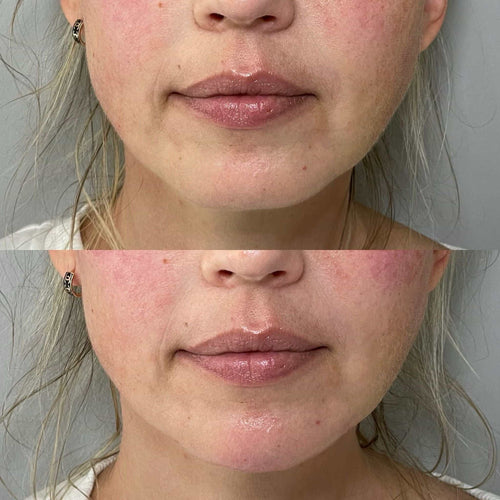
- The Labiomental Groove contributes significantly to facial attractiveness and expression. A well-defined groove can create a more symmetrical and proportionate face, while an indentation or absence of the groove may detract from overall aesthetic appeal.
- The way individuals use their Labiomental Groove during expression also reveals their personality and emotional state. For example, a shallow groove may indicate relaxation, while a deeper indentation can suggest anxiety or stress.
Conclusion:
The Labiomental Groove is a complex feature that plays a vital role in both the functional and aesthetic aspects of human communication and expression. Its unique function as an articulatory pathway, combined with its influence on facial aesthetics, highlights the importance of this anatomical structure.
Muscle Attachment
The labiomental groove, also known as the chin dimple, is a small indentation located on either side of the lower lip, just below the mouth. This anatomical feature is relatively common and can be found in approximately 20-50% of the human population.
From a physiological standpoint, the labiomental groove serves several purposes. Firstly, it provides a site for the attachment of muscles that control facial expressions. The mentalis muscle, which runs from the chin to the lower lip, has two parts: the superficial and deep heads. The superficial head attaches to the skin above the labiomental groove, while the deep head inserts into the underlying bone. This allows for precise control over the movement of the lower lip.
Another function of the labiomental groove is to facilitate the transmission of forces from the mentalis muscle to the mandible (lower jawbone). When the person makes a facial expression, such as puckering up or clenching the jaw, the mentalis muscle contracts and pulls on the skin above the labiomental groove. This creates a localized pressure increase that is transmitted to the mandible, allowing for precise control over the movement of the lower lip and chin.
From an evolutionary perspective, the labiomental groove may have played a role in the development of certain facial expressions and communication behaviors. For example, some researchers have suggested that the ability to form a dimple or a small indentation on either side of the mouth may be an indicator of emotional intelligence or social status.
From a clinical perspective, the labiomental groove can provide clues about underlying anatomical structures. For instance, abnormalities in the shape or depth of the groove can be indicative of conditions such as mandibular dysfunction, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, or even neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
Interestingly, the labiomental groove has also been studied in relation to facial aesthetics. Some surgeons and plastic surgeons use this feature as a reference point for procedures aimed at improving the appearance of the chin or lower lip. The groove can also serve as a landmark for injectable fillers or other cosmetic treatments.
Furthermore, the labiomental groove has been the subject of research in speech pathology and phonetics. For example, studies have investigated how the shape and size of this feature affect articulation and sound production, particularly in relation to certain consonant sounds like “k” and “g”.
In addition, the labiomental groove has also been associated with other facial features, such as the presence or absence of dimples. Research has shown that people with prominent lip lines may be more likely to have a higher concentration of sebaceous glands in this area, which can contribute to acne or rosacea.
From an artistic perspective, the labiomental groove has inspired many sculptors and artists throughout history. For example, famous sculptures like Michelangelo’s “David” feature prominent facial features, including a well-defined chin and labiomental groove. This focus on anatomical detail reflects a deep understanding of the human body and its proportions.
Overall, the labiomental groove is a complex and multifaceted feature that plays important roles in various aspects of anatomy, physiology, evolution, and aesthetics. Its study continues to shed light on the intricacies of the human face and our ability to communicate with others through facial expressions.
- The mentalis muscle, which runs from the chin to the lower lip, has two parts: the superficial and deep heads.
- The labiomental groove serves as a site for the attachment of muscles that control facial expressions.
- The groove facilitates the transmission of forces from the mentalis muscle to the mandible.
- Abnormalities in the shape or depth of the groove can be indicative of conditions like mandibular dysfunction, TMJ disorders, or neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
- The labiomental groove has been studied in relation to facial aesthetics and can serve as a landmark for injectable fillers or other cosmetic treatments.
- Research on the labiomental groove has also investigated its association with other facial features, such as dimples and lip lines.
A thorough understanding of the labiomental groove highlights the intricate relationships between various anatomical structures in the human face. By studying this feature, researchers can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of human anatomy and its impact on our daily lives.
The labiomental groove provides an attachment point for the mentalis muscle, which helps to form the lower lip and contribute to facial movements such as pursing or puckering.
The labiomental groove is a small, V-shaped depression found on the lower lip between the mental protrusion and the commissure, where the two halves of the lower lip meet. It serves as an attachment point for the mentalis muscle, which plays a crucial role in forming the shape of the lower lip and facilitating various facial movements.
The labiomental groove is relatively small and can be difficult to visualize on a single image, but its significance lies in its function as a key component of the musculature that controls the movement of the lower lip. The mentalis muscle, which originates from the mental region of the chin, runs from the skin over the mental protuberance down to the labiomental groove. From here, it inserts into the skin of the lower lip.
By acting as an attachment point for the mentalis muscle, the labiomental groove enables the precise control of the movement of the lower lip. The muscle can contract or relax to varying degrees, depending on the individual’s needs, allowing for a range of expressions and movements, including pursing or puckering. This complex interplay between muscles allows for nuanced communication and expression.
Furthermore, the labiomental groove plays a role in the overall symmetry of the face. When the mentalis muscle contracts to form the lower lip, it helps maintain an even tension between the two halves of the lip. This ensures that expressions such as smiling or frowning are symmetrical and visually appealing.
Interestingly, abnormalities in the labiomental groove can impact facial expression and movement. Individuals with conditions such as mandibular dysgenesis or other forms of craniofacial anomalies may have variations in the shape or size of this groove, which can affect their ability to form certain lip movements or expressions.
From a clinical perspective, understanding the significance of the labiomental groove has implications for orthodontics and facial reconstruction. For example, surgeons may consider the location and structure of this groove when planning procedures such as a lower lip resection or other forms of facial surgery.
In summary, the labiomental groove is an often-overlooked yet crucial component of the musculature that controls the movement of the lower lip. Its role in facilitating precise control over facial expressions and maintaining symmetry highlights its importance in understanding human anatomy and communication.
Facial Expression and Aesthetics
The Labiomental Groove, also known as the marionette smile, is a subtle yet distinctive facial feature that runs from the mouth down to the chin.
It’s a small, linear depression in the lower lip, typically found on individuals with European or Mediterranean ancestry.
This groove can vary in depth and shape depending on factors such as genetics, age, and emotional state.
From an aesthetic perspective, the Labiomental Groove is often considered a defining characteristic of certain facial types, including the “heart-shaped” face.
Individuals with this feature are said to possess a more angular or pointed chin, with a well-defined jawline and prominent facial bones.
- Aesthetically, the Labiomental Groove is often associated with a more feminine or elegant appearance.
- It’s also sometimes linked to a more dramatic or expressive face shape, allowing for greater range of emotions to be conveyed through subtle variations in lip movement and facial tension.
From an evolutionary perspective, the Labiomental Groove may serve as a visual indicator of emotional state or intentions.
For instance, a prominent groove can suggest that an individual is experiencing strong emotions such as excitement, joy, or even aggression.
On the other hand, a less pronounced groove may imply that someone is more reserved or calm in their demeanor.
- Facial expressions and emotions are often conveyed through complex interactions between various facial muscles, including those surrounding the mouth and lips.
- The Labiomental Groove plays a significant role in modulating these expressions, as it can either accentuate or soften the lines of the face based on its depth and angle.
Interestingly, research has shown that the perception of facial attractiveness is influenced by various factors, including symmetry, balance, and distinctive features like the Labiomental Groove.
Studies have also explored the relationship between this groove and emotional intelligence, suggesting that individuals with more prominent grooves may possess greater empathy and social awareness.
- More research is needed to fully understand the significance of the Labiomental Groove in human communication and aesthetics.
- However, its impact on our perception of facial attractiveness, emotional expression, and overall aesthetic appeal cannot be overstated.
According to a study published by researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), the labiomental groove plays a significant role in shaping facial expressions and aesthetics. The groove can affect the way the lips curve downwards during an frown or upwards during a smile.
The labiomental groove, also known as the marionette lines, is a facial feature that runs from the edge of the mouth to the chin.
According to a study published by researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), the labiomental groove plays a significant role in shaping facial expressions and aesthetics.
The researchers found that the depth and width of the groove can affect the way the lips curve downwards during an frown or upwards during a smile.
The study also suggests that the labiomental groove can influence the perceived attractiveness of a person’s face.
The groove is formed by the intersection of the mentalis muscle, which runs from the chin to the corner of the mouth, and the depressor anguli oris muscle, which runs from the angle of the jaw to the corner of the mouth.
The labiomental groove can be measured using a variety of techniques, including 3D scanning and photogrammetry.
The researchers found that the depth and width of the groove are influenced by a range of factors, including genetics, age, sex, and ethnicity.
For example, women tend to have deeper labiomental grooves than men, and individuals with darker skin tones may have more pronounced grooves due to the way melanin interacts with light.
The study also found that the labiomental groove can be affected by a range of environmental factors, including facial expressions, emotions, and even social media use.
For instance, repeated expressions of sadness or disgust can lead to deeper grooves over time, while smiling regularly can cause them to fade.
The significance of the labiomental groove extends beyond aesthetics, however; it also plays a role in facial communication and expression.
The study found that individuals with more pronounced labiomental grooves are often perceived as more expressive and emotional, while those with shallower grooves may be seen as less emotive.
Furthermore, the labiomental groove can influence social interaction and relationships; for example, someone with a deeper groove may be more likely to be perceived as trustworthy or authentic.
- The study’s findings have implications for fields such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology, where facial expressions and aesthetics are used to understand social behavior and relationships.
- The labiomental groove may also be relevant in the context of facial reconstruction or plastic surgery, where surgeons may use it as a reference point when reconstructing damaged or disfigured faces.
- Additionally, the study’s findings can inform our understanding of the role of genetics and environmental factors in shaping facial features and aesthetics.
Medial and Surgical Considerations
The Labiomental Groove, also known as the chin dimple or marionette fold, is a small anatomical groove located at the corner of the mouth, specifically on either side of the chin.
It is characterized by a slight indentation or crease on the skin that forms when one smiles or frowns, and it can be more noticeable in some individuals than others due to various factors such as genetics, muscle tone, and facial structure.
The Labiomental Groove serves several purposes:
- It helps to frame the smile by creating a natural-looking curve of the lips and chin.
- It can add depth and dimension to the face, making it more aesthetically pleasing.
- It is also a key feature in facial expressions, as it conveys emotions such as happiness, sadness, or surprise.
Surgically, the Labiomental Groove can be considered for various reasons:
- To correct asymmetrical facial features or uneven lip lines.
- To enhance the overall appearance of the chin and mouth area.
- To restore a natural-looking curve to the lips and face.
- To address facial muscle imbalances that can affect the Labiomental Groove.
Medially, the Labiomental Groove is often considered in conjunction with other facial features to achieve a more harmonious balance:
- The position of the nasolabial fold (the crease between the nose and mouth).
- The shape and size of the lips.
- The overall symmetry of the face.
Surgical consideration for correction often involve techniques such as:
- Facelifts to address underlying muscle tension or sagging skin.
- Lip augmentation or lip fillers to enhance the appearance of the lips and mouth area.
- Facial implants to correct asymmetrical facial features or uneven bone structure.
The Labiomental Groove is an important aspect of facial aesthetics, and its significance extends beyond mere cosmetic considerations:
- It can be a key indicator of overall facial health and muscle function.
- Its presence or absence can be influenced by various factors such as genetics, diet, and lifestyle.
A thorough understanding of the Labiomental Groove is essential for effective surgical correction and aesthetic enhancement:
- Surgeon must consider the individual’s facial structure, muscle tone, and overall health before recommending or performing surgery.
- Patient should undergo a comprehensive evaluation to determine the best course of treatment.
In medical contexts, the labiomental groove may be of interest to surgeons who are considering procedures such as facial rejuvenation or lip augmentation. The groove’s location and relationship with surrounding structures can impact surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
The labiomental groove, also known as the marionette fold or labiomental crease, is a natural indentation found on the face, specifically on the lower lip and chin. It serves as a hinge point for the lower lip, allowing it to move up and down with each expression.
Anatomically, the labiomental groove is located between the mental nerve, which runs along the lower border of the mandible (jawbone), and the facial vein, which ascends towards the external jugular vein. This positioning creates a natural fold or crease in the skin, which can be more pronounced in some individuals than others.
In medical contexts, the labiomental groove may be of interest to surgeons who are considering procedures such as facial rejuvenation or lip augmentation. The groove’s location and relationship with surrounding structures can impact surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
A thorough understanding of the labiomental groove is essential for any surgical intervention in this region. Surgeons must take into account the anatomy of the area, including the position and depth of the groove, as well as its relationship to nearby blood vessels and nerves.
Proper identification and evaluation of the labiomental groove are crucial for surgeons to achieve optimal results in procedures such as:
* Facial rejuvenation: The labiomental groove can be a significant factor in determining the outcome of facial rejuvenation surgery, particularly when it comes to lip augmentation or lower face lifting.
* Lip augmentation: The location and depth of the labiomental groove can impact the success of lip augmentation procedures, as it may affect the visibility and durability of the implant.
Additionally, knowledge of the labiomental groove is essential for surgeons to minimize complications and ensure patient satisfaction. This includes avoiding surgical incisions that might compromise the integrity of the groove or nearby structures, and taking steps to promote healing and restore natural movement to the lower lip.
* Skin laxity: The labiomental groove can be a significant contributor to skin laxity in the lower face, particularly during facial rejuvenation. Understanding its relationship with surrounding tissues is essential for surgeons to develop effective treatment plans.
Furthermore, awareness of the labiomental groove’s significance extends beyond surgical interventions. In cosmetic and reconstructive contexts, understanding its anatomy can help professionals to better counsel patients on their expectations and outcomes.
* Lip enhancement: The natural appearance of the labiomental groove is a key consideration when it comes to lip enhancement procedures. Surgeons must take into account the potential impact of surgical or non-surgical treatments on this feature.
Moreover, knowledge of the labiomental groove’s function and significance can also inform non-surgical treatments and cosmetic interventions, such as facial fillers or chemical peels.
* Facial aesthetics: The natural contours of the face, including the labiomental groove, play a significant role in determining facial attractiveness. Understanding its anatomy and relationship to surrounding structures is essential for professionals working in fields related to facial aesthetics.
Ultimately, a thorough understanding of the labiomental groove is necessary to provide optimal care for patients undergoing surgical or non-surgical interventions in this region. By recognizing its significance, medical professionals can better address patient concerns and achieve more satisfying outcomes.
* Precision surgery: The labiomental groove’s location and relationship with surrounding tissues require precision and attention to detail when it comes to surgical procedures.
Read more about Decléor Direct here. Read more about Mind Plus Motion here. Read more about En Bloch Hotels here. Read more about Raindrops and Ribbons here. Read more about Made by Penny here. Read more about Andrea McGinty Art here.
- Why Are Kratom Gummies So Popular In Wellness Circles? - November 5, 2025
- What Is Tear Trough Filler Good For - November 4, 2025
- Weed Infused Juices For The Win - November 1, 2025
